Environmental Hydraulics Research Group
managing stream, river, wetland, and groundwater hydraulics to benefit humans and ecosystems
Research
We are interested in how river management and infrastructure
affect movement of water through river corridors, and how these in
turn affect human and natural communities downstream. Relevant
science topics include river-floodplain and surface
water-groundwater interaction, while applied topics include flooding
and flood control, river/stream restoration, water quality and
pollutant removal, ecosystem health and ecological uplift, and
hydropower. We seek out relationships between driving
factors and system response, noting nonlinearities and how they can
be used to optimize engineering design and sustainable landscape management.
Recent Research Areas
-
Restoration of surface water-groundwater and floodplain exchange in streams, rivers, and wetlands
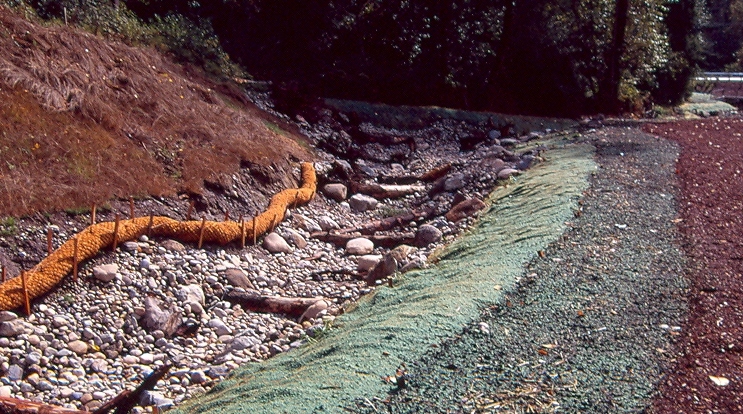


This research area is evaluating the potential value of restoring hyporheic exchange and floodplain exchange (creation of riverine wetlands) as a part of stream/river restoration projects. Key benefits may include flood reduction, baseflow augmentation, nutrient processing, and thermal mitigation, benefitting both ecological and human health in river systems.
Collaborators: Durelle Scott, Cully Hession, Mike Gooseff
Students: Elizabeth Cranmer, David Azinheira, Christopher Guth, Masud Rana, Benjamin Hammond, Kristen Brooks, Michael Calfe, Carly Federman, Luke Goodman, Morgan Oehler, Dario Tarifa, Abby Knauer
Support: National Science Foundation (ENG-CBET-Environmental Sustainability), Award#1066817; Core Fulbright Scholar Award to Taiwan, "Effect of Floodplain Inundation on River Pollution in Taiwan’s Strong Monsoonal Climate;" Chesapeake Bay Trust, Awards #18006, 25735; AAAS Science and Technology Policy Fellowship.
We have also gotten support from several NSF REU programs. One produced an excellent website with flood experiment results.
Publications:
Federman, C.E., D.T. Scott, and E.T. Hester. 2023. Impact of floodplain and Stage 0 stream restoration on flood attenuation and floodplain exchange during small frequent storms. Journal of the American Water Resources Association 59:29–48. Link to open access article.
Hester, E.T., B. Hammond, and D.T. Scott. 2016. Effects of inset floodplains and hyporheic exchange induced by in-stream structures on nitrate removal in a headwater stream. Ecological Engineering 97:452-464.
Calfe, M.L., D.T. Scott, Hester, E.T. 2022. Nitrate removal by watershed-scale hyporheic stream restoration: Modeling approach to estimate effects and patterns at the stream network scale. Ecological Engineering, 175: 106498.
Hester, E.T., A.Y.-C. Lin, and C.W. Tsai. 2020. Effect of floodplain restoration on photolytic removal of pharmaceuticals. Environmental Science & Technology 54, 3278−3287.
Hester, E.T., K.E. Brooks and D.T. Scott. 2018. Comparing reach scale hyporheic exchange and denitrification induced by instream restoration structures and natural streambed morphology. Ecological Engineering 115:105-121.
Keys, T.A., H. Govenor, C.N. Jones, W.C. Hession, E.T. Hester, and D.T. Scott. 2018. Effects of large wood on floodplain connectivity in a headwater Mid-Atlantic stream. Ecological Engineering 118:134-142.
Rana, SM.M., D.T. Scott, and E.T. Hester. 2017. Effects of in-stream structures and channel flow rate variation on transient storage. Journal of Hydrology 548:157-169.
Hester, E.T., C.R. Guth, D.T. Scott, and C.N. Jones. 2016. Vertical surface water-groundwater exchange processes within a short residence time floodplain induced by experimental floods along a headwater stream. Hydrological Processes 30(21):3770–3787.
Jones, C.N., D.T. Scott, C.R. Guth, E.T. Hester, and W.C. Hession. 2015. Seasonal variation in floodplain biogeochemical processing in a restored headwater stream. Environmental Science & Technology 49(22):13190−13198.
Azinheira, D.L., D.T. Scott, W.C. Hession, and E.T. Hester. 2014. Comparison of effects of inset floodplains and hyporheic exchange induced by in-stream structures on solute retention. Water Resources Research 50(7):6168-6190.
Hester, E.T., and E.N. Cranmer. 2014. Variation of hyporheic exchange potential among urban region streams: implications for stream restoration. Environmental & Engineering Geoscience 20(3):287-304.
Hester, E.T. and M.N. Gooseff. 2011. Hyporheic restoration in streams and rivers. Chapter in Stream Restoration in Dynamic Fluvial Systems: Scientific Approaches, Analyses, and Tools (Simon, A., S.J. Bennett, and J.M. Castro, Eds.).
Hester, E.T., and M.N. Gooseff. 2010. Moving Beyond the Banks: Hyporheic Restoration Is Fundamental to Restoring Ecological Services and Functions of Streams. Environmental Science & Technology 44(5):1521-1525. Link to open access article.
-
Measuring environmental sustainability of water resources management in watersheds
This research area is working to develop comprehensive yet feasible metrics for quantify environmental sustainability of water resources management within watersheds.
Collaborators: John Little, Cayelan Carey
Publications:
Amaya, M., F. Duchin, E.T. Hester, and J.C. Little. 2022. Applying a coupled hydrologic-economic modeling framework: Evaluating conjunctive use strategies for alleviating seasonal watershed impacts caused by agricultural intensification. Frontiers in Water 4:913501.
Amaya, M., F. Duchin, E.T. Hester, and Little, J.C. 2022. Applying a coupled hydrologic-economic modeling framework: Evaluating alternative options for reducing impacts for downstream locations in response to upstream development. Sustainability, 14:6630.
Little, J.C., E.T. Hester, S. Elsawah, G.M. Filz, A. Sandu, C.C. Carey, T. Iwanaga, and A.J. Jakeman. 2019. A tiered, system-of-systems modeling framework for resolving complex socio-environmental policy issues. Environmental Modelling and Software 112:82-94.
Little, J. C., E.T. Hester, and C.C. Carey. 2016. Assessing and enhancing environmental sustainability - A conceptual review. Environmental Science & Technology 50(13):6830-6845.
Hester, E.T., and J.C. Little. 2013. Measuring environmental sustainability of water in watersheds. Environmental Science & Technology 47(15):8083-8090. Link to feature.
-
Natural attenuation of pollutants at the surface water-groundwater interface in rivers
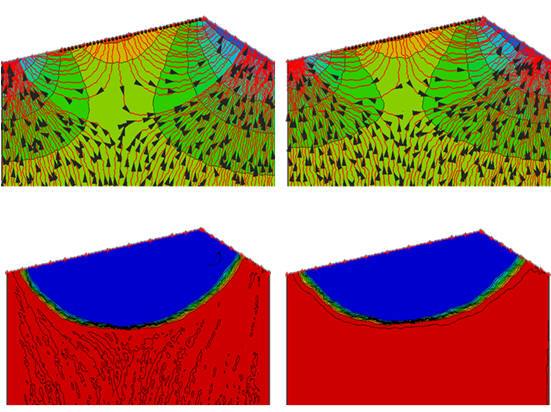
This research area is utilizing numerical modeling and laboratory experiments to evaluate controls on mixing and pollutant attenuation of contaminants in the hyporheic zone beneath riverbed dunes. Applied benefits may include accounting for these affects in monitored natural attenuation, or active promotion of beneficial reactions through sustainable practices such as carbon augmentation through riparian planting.
Collaborators: Mark Widdowson, Bayani Cardenas, Roy Haggerty, Sourabh Apte
Students: Katie Young, Abenezer Nida, Katherine Santizo, Lauren Eastes, Seth Lotts
Support: National Science Foundation (ENG-CBET-Environmental Engineering), Award#1437021; U.S. Department of Energy, Subsurface Biogeochemical Research (SBR), Award DE-SC0021402.Publications:
Monterroso, H., M. A. Widdowson, W. S. Lotts, K. B. Strom, and E. T. Hester. 2024. Effects of boundary hydraulics, dissolved oxygen, and dissolved organic carbon on growth and death dynamics of aerobic microbes in riverbed dune-induced hyporheic zones. Science of the Total Environment 906:167401
Santizo, K.Y., M.W. Widdowson, and E.T. Hester. 2022. Numerical modeling of an abiotic hyporheic mixing-dependent reaction: Chemical evolution of mixing and reactant production zones. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 251:104066.
Hester, E.T., K.Y. Santizo, A.A. Nida, and M.A. Widdowson. 2021. Hyporheic transverse mixing zones and dispersivity: Laboratory and numerical experiments of hydraulic controls. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 243: 103885.
Santizo, K.Y., M.A. Widdowson, and E.T. Hester. 2020. Abiotic mixing-dependent reaction in a laboratory simulated hyporheic zone. Water Resources Research 56, e2020WR027090.Hester, E.T., L.A. Eastes, and M.A. Widdowson. 2019. Effect of surface water stage fluctuation on mixing-dependent hyporheic denitrification in riverbed dunes. Water Resources Research 55(6):4668-4687.
Hester, E.T., M.B. Cardenas, R. Haggerty, and S.V. Apte. 2017. The importance and challenge of hyporheic mixing. Water Resources Research 53(5):3565-3575.
Hester, E.T., K.I. Young, and M.A. Widdowson. 2014. Controls on mixing-dependent denitrification in hyporheic zones induced by riverbed dunes: a steady-state modeling study. Water Resources Research 50(11):9048-9066.
Hester, E.T., K.I. Young, and M.A. Widdowson. 2013. Mixing of surface and groundwater induced by riverbed dunes: implications for hyporheic zone definitions and pollutant reactions. Water Resources Research 49:5221–5237.
-
Preferential flow at the surface water-groundwater interface in streams and rivers
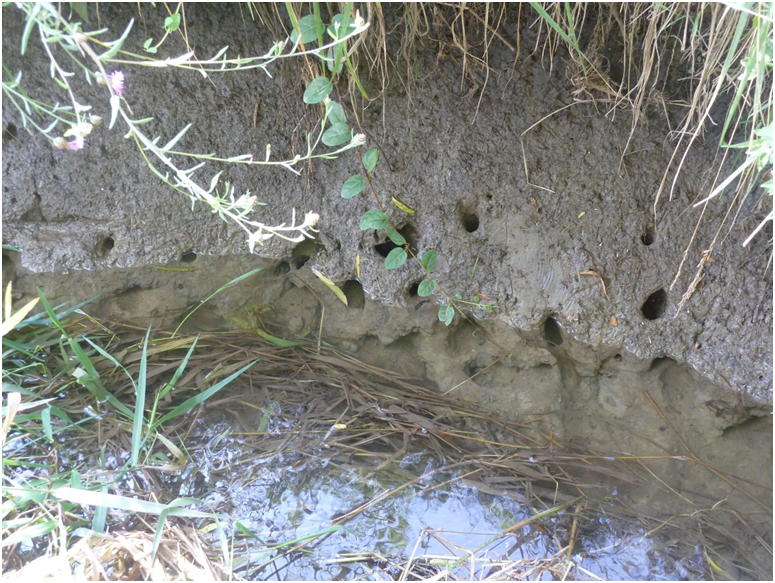

This research area is evaluating the significance of preferential flow for surface water-groundwater exchange in stream and river systems. We are interested in the exchange of water as well as pollutants.
Collaborators: Adam Ward, Durelle Scott
Students: Garrett Menichino, Amiana McEwen, Seth Lotts
Support: National Science Foundation (GEO-EAR-Hydrologic Sciences), Award#1446481, Jeffress Memorial Trust, Consortium of Universities for the Advancement of Hydrologic Science, Inc. (CUAHSI) Hydrogeophysics Travel Grant, Institute for Critical Technology and Applied Science (ICTAS) at Virginia Tech
Publications:
Lotts, W.S., and E.T. Hester. 2023. Take it to the bank: A numerical examination of the effects of soil pipes on bypass of riparian buffer nitrate removal capacity. Journal of Hydrology 616:128821.
Lotts, W. S., and E.T. Hester. 2022. Pipe dreams: The effects of stream bank soil pipes on hyporheic denitrification caused by a peak flow event. Water Resources Research, 58, e2021WR030312. Link to open access article.
Hester, E.T., and G.A. Fox. 2020. Preferential flow in riparian groundwater: Gateways for watershed solute transport and implications for water quality management. Water Resources Research, 56, e2020WR028186. Link to open access article.
Hester, E.T., A.M. McEwen, B. Kim, and E. Rost. 2020. Abundance, distribution, and geometry of naturally occurring streambank soil pipes. Freshwater Science 39(4):735–751.
Lotts, W.S., and E.T. Hester. 2020. Filling the void: the effect of streambank soil pipes on transient hyporheic exchange during a peak flow event. Water Resources Research 56(2), e2019WR025959. Link to open access article.
Menichino, G.T., and E.T. Hester. 2015. The effect of macropores on bi-directional exchange between stream channels and bank groundwater. Journal of Hydrology 529(3):830-842.
Menichino, G.T., D.T. Scott, and E.T. Hester. 2015. Abundance and dimensions of naturally occurring macropores along stream channels and the effects of artificially constructed large macropores on transient storage. Freshwater Science 4(1):125–138. Invited article to special issue.
Menichino, G.T., A.S. Ward, and E.T. Hester. 2014. Macropores as preferential flow paths in meander bends. Hydrological Processes 28(3):482-495.
-
Hydropower
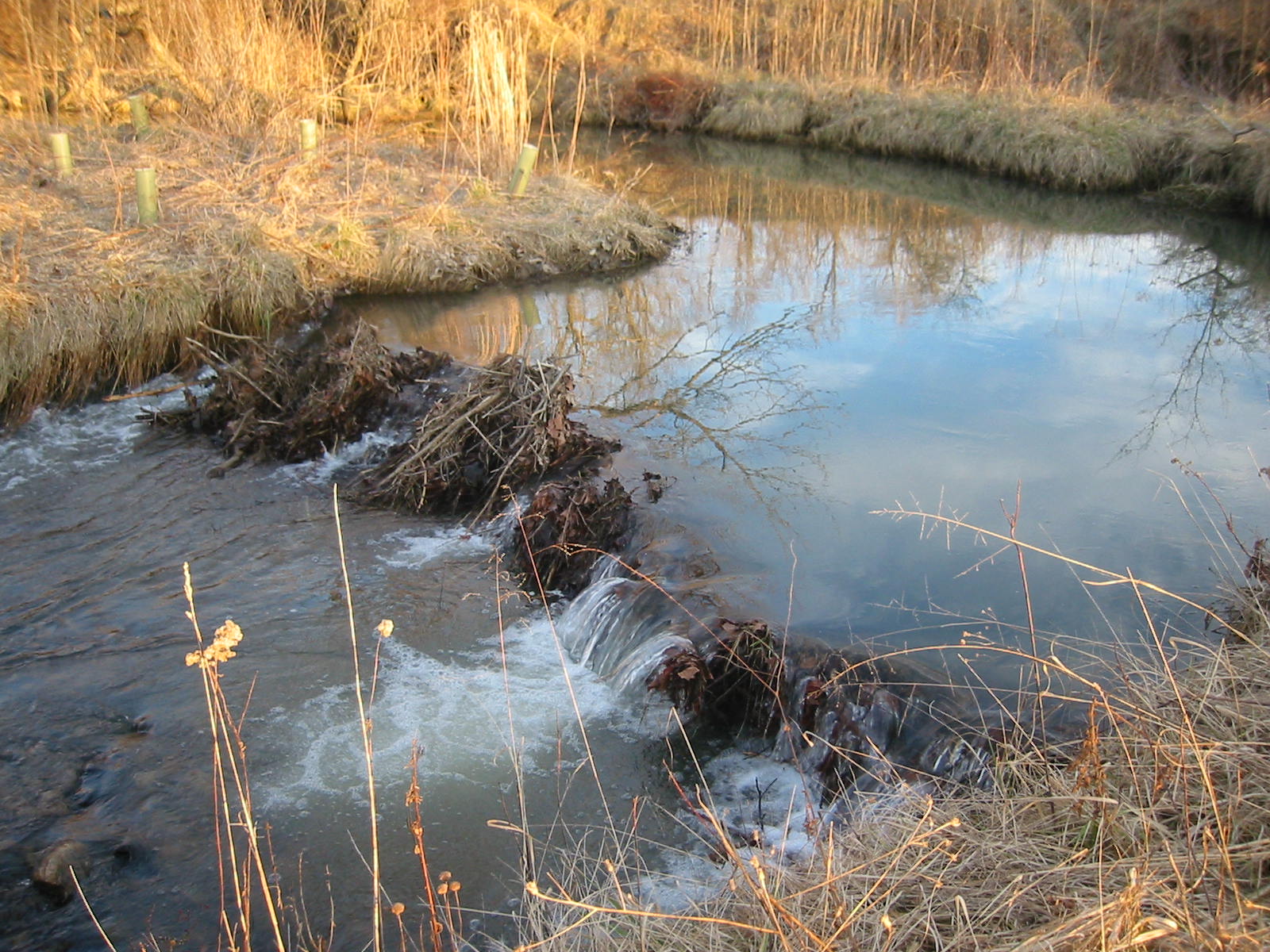

This research area seeks to understand how to enhance the compatibility of hydropower generation with environmental and human concerns such as clean water and healthy ecosystems. A particular focus is how river restoration may assist in mitigating effects of hydrologic change and benefit both hydropower and ecosystems. On a small scale, we have undertaken a series of feasibility studies for micro-hydropower facilities for various private clients in Virginia. In addition to hydraulic feasibility, these projects have also assessed potential impacts to riverine habitat. We are also involved in larger-scale efforts to understand effects of tributary habitat restoration on hydropower generation in the context of hydrologic change.
Collaborators: Nathalie Voisin, Natalie Griffiths, Shih-Chieh Kao
Support: U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Water Power Technologies Office (WPTO) through the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) Science and Technology Policy Fellowship (STPF)
Publications:
Hester, E. T., N. Voisin, N. A. Griffiths, and S.-C. Kao. 2025. Intersection of hydrologic change and hydropower in the United States: Needs for future research and practice. Journal of the American Water Resources Association 61:e70020.